Know Your Brain: Red Nucleus
Where is the red nucleus?
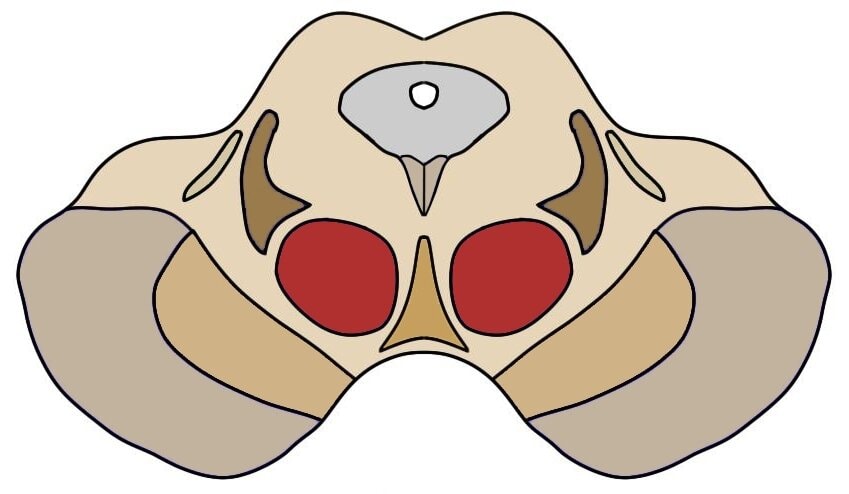
The red nucleus is found in a region of the brainstem called the midbrain. There are actually two red nuclei—one on each side of the brainstem.
The red nucleus can be subdivided into two structures that are generally distinct in function: the parvocellular red nucleus, which mainly contains small and medium-sized neurons, and the magnocellular red nucleus, which contains larger neurons. The red nucleus is recognizable immediately after dissection because it maintains a reddish coloring. This coloring is thought to be due to iron pigments found in the cells of the nucleus.
What is the red nucleus and what does it do?
As mentioned above, the red nucleus can be subdivided into two structures with separate functions: the parvocellular red nucleus and the magnocellular red nucleus. In the human brain, most of the red nucleus is made up of the parvocellular red nucleus, or RNp; the magnocellular red nucleus (RNm) is not thought to play a major role in the adult human brain. In four-legged mammals (e.g., cats, mice), however, the RNm is a more prominent structure—in both size and importance.
Neurons from the cerebellum project to the RNm, and RNm neurons leave the red nucleus and form the rubrospinal tract, which descends in the spinal cord. In animals that walk on four legs, this pathway is activated around the time of voluntary movements; it seems to play an important role in walking, avoiding obstacles, and making coordinated paw movements. RNm neurons, however, also respond to sensory stimulation, and may provide sensory feedback to the cerebellum to help guide movements and maintain postural stability.
In primates that mainly walk on two legs (including humans), the RNm is not thought to play a large role in walking and maintaining postural stability, as other tracts (e.g., the corticospinal tract) take over such functions. The RNm, however, does appear to be involved in controlling hand movements in humans and other primates. Interestingly, the RNm is more prominent in the human fetus and newborn, but regresses as a child ages, which may have to do with the development of corticospinal tract and the ability to walk on two legs.
Despite its relatively greater import in the human brain, the RNp is poorly understood, as its diminished presence in other animals makes it more difficult to study using an animal model. Neurons from motor areas in the prefrontal cortex and premotor cortex, as well as neurons from nuclei in the cerebellum known as the deep cerebellar nuclei, extend to the RNp. There is also a collection of neurons that leave the RNp and travel to the inferior olivary nucleus, which communicates with the cerebellum and is thought to be involved in the control of movement. A number of proposed functions have been attributed to these connections between the RNp, cerebellum, and inferior olivary nucleus, such as movement learning, the acquisition of reflexes, and the detection of errors in movements. But the precise function of these pathways—and thus the RNp’s role in them—is still not clear.
Several studies have found the red nucleus to play a role in pain sensation as well as analgesia. The latter might be due to connections between the red nucleus and regions like the periaqueductal gray and raphe nuclei, which are part of a natural pain-inhibiting system in the brain.
In terms of pathology, dysfunction in the human red nucleus has been linked to the development of tremors, and is being investigated as playing a potential role in Parkinson’s disease. Damage to the red nucleus has also been associated with a number of other problems with movement and muscle tone.
References (in addition to linked text above):
Basile GA, Quartu M, Bertino S, Serra MP, Boi M, Bramanti A, Anastasi GP, Milardi D, Cacciola A. Red nucleus structure and function: from anatomy to clinical neurosciences. Brain Struct Funct. 2021 Jan;226(1):69-91. doi: 10.1007/s00429-020-02171-x. Epub 2020 Nov 12. PMID: 33180142; PMCID: PMC7817566.
Vadhan J, M Das J. Neuroanatomy, Red Nucleus. 2020 Jul 31. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan–. PMID: 31869092.